Applications
Cell Therapy
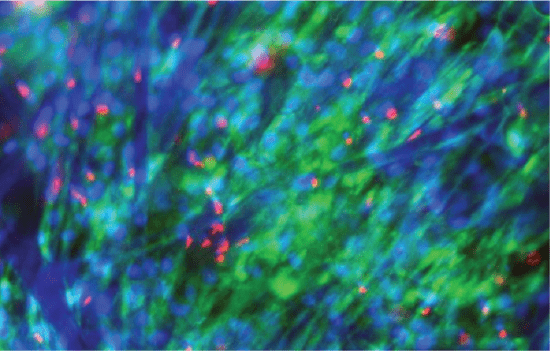
Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) in BioNOC™ II macrocarriers
(Green: cytoplasm; Blue: nucleus all cells; Red: nucleus dead cells)
Advances in immunotherapy for human oncology provide an alternative and/or augmentation to chemotherapeutic treatments. This is also true for animals as the immunological elements are similar to humans.
In response to canine cancer, several cell-based immunotherapies are developed including tumor-specific lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. In one study, anti-CD3 mAb and human cytokines were used for the expansion of cytotoxic T cells but were not tumor-specific. In another study by MD Anderson Cancer center, HER-2 CAR T cells were demonstrated to target and kill canine osteosarcoma cell line. NK cells isolated from blood lymphocytes can lead to tumor regression for osteosarcoma, as shown by researchers at UC Davis.
In response to canine cancer, several cell-based immunotherapies are developed including tumor-specific lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. In one study, anti-CD3 mAb and human cytokines were used for the expansion of cytotoxic T cells but were not tumor-specific. In another study by MD Anderson Cancer center, HER-2 CAR T cells were demonstrated to target and kill canine osteosarcoma cell line. NK cells isolated from blood lymphocytes can lead to tumor regression for osteosarcoma, as shown by researchers at UC Davis.
Human medicine has also come far in terms of stem cell therapy with the development of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). At North Carolina State University, autologous HSCs harvested using apheresis machine are being used to treat dogs with B- and T-cell lymphoma with remarkable efficacy. MSCs, on the other hand, has been extensively used for translational researches including dogs, cats, rabbits, horse, pigs, cows, and small ruminants. Further application of stem cells is discussed in the joint support section.





