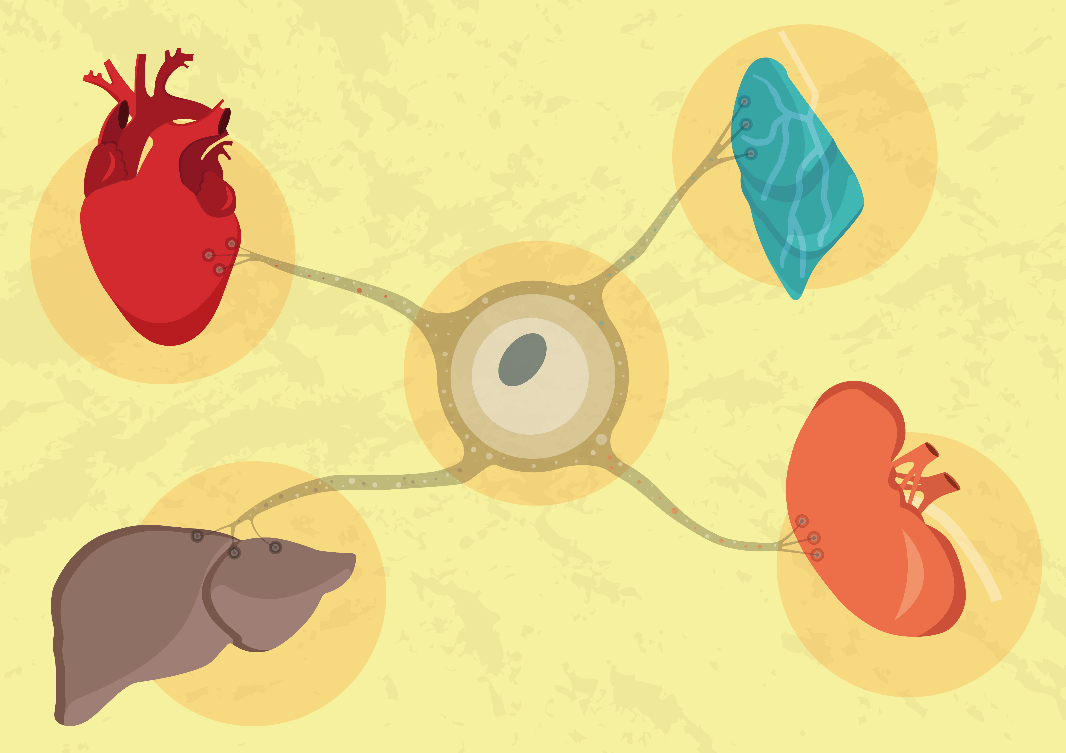
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are derived from skin or blood cells that have been reprogrammed into an embryonic stem-cell like cells capable of differentiating into various human cells for therapeutic purposes. This new technology is an interesting field in medicine, not only for its potential in disease modelling but also for its capability to regenerate and repair damaged tissues.
Disease modelling and gene Therapy
iPSC disease models can be generated through the reprogramming of isolated human fibroblasts. Reprogramming of the fibroblasts can be achieved by using viral vectors capable of integrating reprogramming factor genes in the fibroblast genome.
Listed below are some diseases modelled via the most commonly used viral vectors - lentivirus and retrovirus vector systems.
|
Lentivirus viral vector |
Retrovirus viral vector |
|
|
Application in regenerative medicine
One promising capability of iPSC is they can be differentiated into a lineage-specific stem cells that will support treatment or tissue regulation. Moreover, the patient's own cells are used to generate these iPSCs to be transplanted to the patient's own body; reducing transplant rejection issues.
iPSCs are traditionally expanded in two-dimensional static cultures. However, this kind of expansion is very limited and have low cell yields. To meet the target number of cells in clinical use, bioreactors are used for cell expansion.
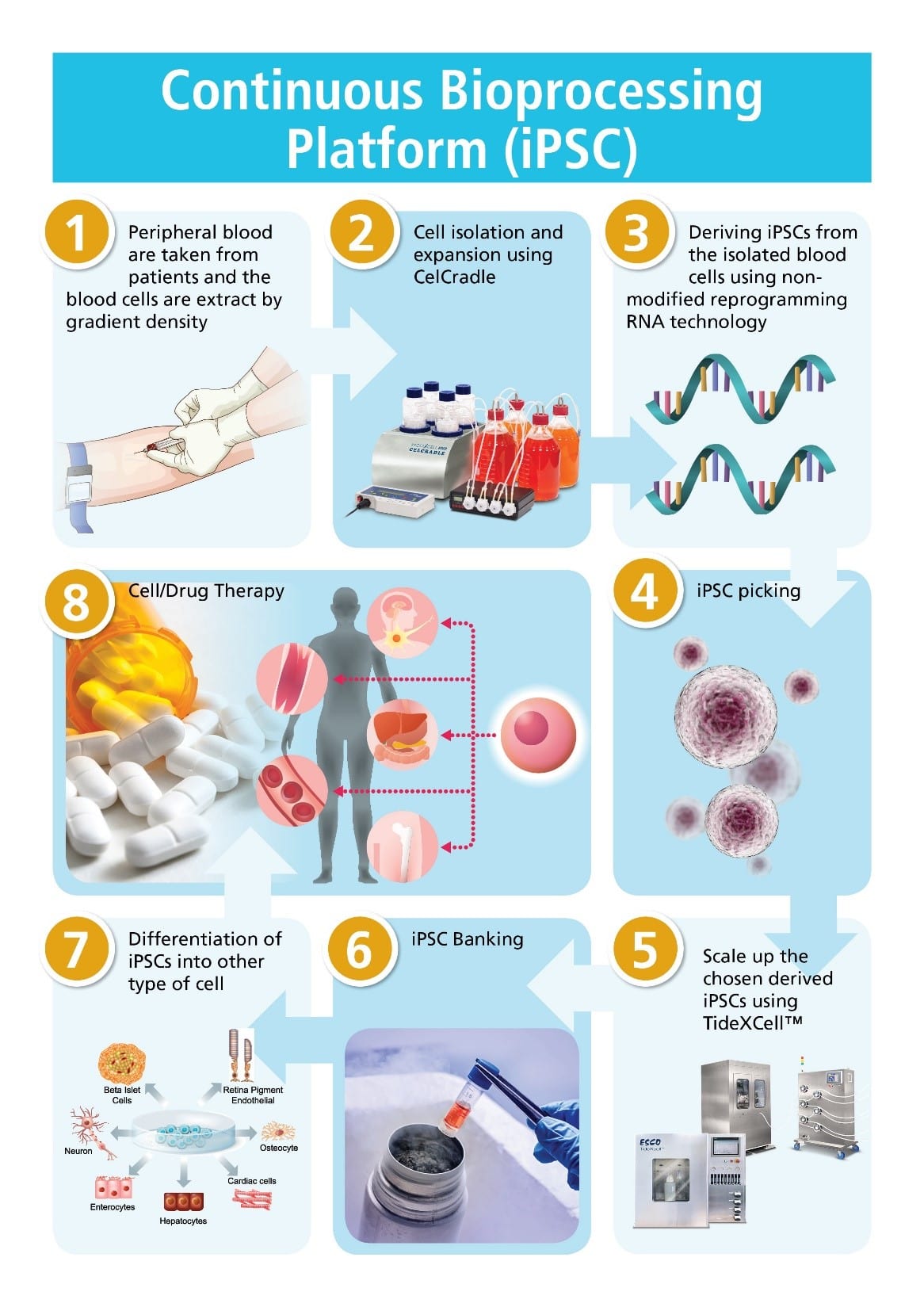
Esco VacciXcell bioreactors are packed-bed bioreactors that can reproduce these induced pluripotent stem cells in large number because of high surface area from the three-dimensional cell culture (BioNOC™ II).
These macroporous carriers are perfect for supporting the growth and proliferation of these adherent cells. These provide suitable environment for iPSC culture that offers better cell-cell communication and let the cells grow at a higher yield. Moreover, these bioreactors operate under Tide Motion principle that enables 100% oxygen and media exchange perfect environment for iPSCs.
Adherent cell culture processing requires more steps and time than suspension. Tide Motion bioreactors offer linearly scalability beginning with research and development up to commercialization to reduce bioprocessing costs and time. Moreover, TideXcell® Cell Harvesting System is a powerful and automated system for harvesting viable cells from 2L to 20L TideXcell® bioreactors. Being a closed system, it is perfect for harvesting seed cells for scaling up without having to worry about contamination.
Reference:
Atoui, R., & Madigan, M. (2018). Therapeutic Use of Stem Cells for Myocardial Infarction. 5(2), 28; doi:10.3390/bioengineering5020028.
Teng M., Jiacheng S., et al. (2017). A brief review: adiposed-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases. 8: 124. 10.1186/s13287-017-0585-3
He S., Nakada D., et al., (2009). Mechanism of Stem Cell Self-renewal. 25:377-406. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.042308.113248.
Esco VacciXcell
21 Changi South Street 1
Singapore 486777
Telephone: +65 6542 0833
Email: [email protected]
About Tide Motion Bioreactors
Tide Motion pertains to the gentle oscillation of culture medium into and out of the matrix vessel that intermittently exposes the cells to aeration and nutrition. The upward oscillation exposes the cells to nutrition, while the downward oscillation exposes the cells to aeration. At the same time, this process washes away products and wastes. This oscillation produces no air bubbles and low shear stress. View a range of products at http://www.vaccixcell.com/tide-technology/
About Esco VacciXcell
Esco VacciXcell is the bioprocessing division of Esco Group of Companies that specializes in the marketing and manufacturing of bioprocessing equipment for cell culture.
Esco VacciXcell provides turnkey manufacturing solutions using its proprietary Tide Motion™ technology to help developing nations to be self-sufficient in the manufacturing, storing, distribution, and administration of vaccines and other biologics, thus providing a complete solution from Discovery to Delivery. For more information on VacciXcell, please visit www.vaccixcell.com
Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest news and updates about our products!
